Paragraph: Consider a simple \(R C\) circuit as shown in Figure \(1\). Process...
Paragraph:
Consider a simple \(R C\) circuit as shown in Figure \(1\).
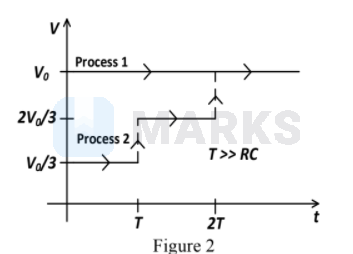
Process 1: In the circuit the switch \(S\) is closed at \(t=0\) and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage \(V_{0}\) (i.e., charging continues for time \(T>>R C\) ). In the process some dissipation \(\left(E_{D}\right)\) occurs across the resistance \(R\). The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is \(E_{C}\).
Process 2: In a different process the voltage is first set to \(\frac{V_{0}}{3}\) and maintained for a charging time \(T>>R C\). Then the voltage is raised to \(\frac{2 V_{0}}{3}\) without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time \(T>>R C\). The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to \(V_{0}\) and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage \(V_{0}\) as in Process 1.
These two processes are depicted in Figure \(2 .\)

Question:
In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance \(E_{D}\) is:
Consider a simple \(R C\) circuit as shown in Figure \(1\).
Process 1: In the circuit the switch \(S\) is closed at \(t=0\) and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage \(V_{0}\) (i.e., charging continues for time \(T>>R C\) ). In the process some dissipation \(\left(E_{D}\right)\) occurs across the resistance \(R\). The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is \(E_{C}\).
Process 2: In a different process the voltage is first set to \(\frac{V_{0}}{3}\) and maintained for a charging time \(T>>R C\). Then the voltage is raised to \(\frac{2 V_{0}}{3}\) without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time \(T>>R C\). The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to \(V_{0}\) and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage \(V_{0}\) as in Process 1.
These two processes are depicted in Figure \(2 .\)


Question:
In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance \(E_{D}\) is:
Solution:
For process (i)
Charge on capacitor
Energy stored in capacitor
Work done by battery
Heat loss
For process (ii)
Charge on capacitor
Extra charge flow through battery
Work done by battery:
Final energy store in capacitor:
Energy store in process 2:
Heat loss in process (ii) = work done by battery in process (ii) – energy store in capacitor process (ii)
For process (iii)
Charge on capacitor
Extra charge flow through battery:
Work done by battery in this process:
Find energy store in capacitor:
Energy stored in this process:
Heat loss in process (iii):
Now total heat loss
Final energy store in capacitor:
So we can say that
Charge on capacitor
Energy stored in capacitor
Work done by battery
Heat loss
For process (ii)
Charge on capacitor
Extra charge flow through battery
Work done by battery:
Final energy store in capacitor:
Energy store in process 2:
Heat loss in process (ii) = work done by battery in process (ii) – energy store in capacitor process (ii)
For process (iii)
Charge on capacitor
Extra charge flow through battery:
Work done by battery in this process:
Find energy store in capacitor:
Energy stored in this process:
Heat loss in process (iii):
Now total heat loss
Final energy store in capacitor:
So we can say that
















 JEE Main
JEE Main JEE Advanced
JEE Advanced NEET UG
NEET UG BITSAT
BITSAT COMEDK
COMEDK VITEEE
VITEEE WBJEE
WBJEE
Join the conversation